AttnED with Explanations
Introduction
Using Encoder-Decoder with Attention Mechanism (AttnED) as the prediction model, and have three post-hoc XAI methods to choose from to explain the model - DiCE, LIME, and SHAP.
Using AttnED with SHAP is accepted at the AI4H Workshop at the 16TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SIGNAL IMAGE TECHNOLOGY & INTERNET BASED SYSTEMS as first author. Check out the publications here. Codes can be found in this GitHub Repo.
How to Use AttnED Package
Define parameters and pre-process the data
ids = 'ID'
date = 'Timestamp'
ordinal_col = ['sClass', 'hProg']
nominal_col = ['Sex']
cont_col = ['Age', 'hVol', 'LonR', 'LatR', 'PTA4', 'Usage']
In this specific case, hearing aid usage is computed with the timestamp parameter using the compute_usage=True argument. get_data.get_processed_data also transforms ordinal and nominal variables with relevant encodings. The aggregate_variables argument transforms the data with a daily frequency. Transform the data with other frequencies will be supported later.
processed_data = get_data.get_processed_data(file,
ids,
date,
ordinal_col,
nominal_col,
groupby='ID',
compute_usage=True,
impute_days=True,
aggregate_variables=True,
remove_outliers=True,
weekday=False)
The get_data.transform_variables function can output three different options depending on the transformed and return_scalar arguments. For example, if original data wished to be obtained for future analysis, then
original_data = get_data.transform_variables(processed_data,
ids,
ordinal_col,
nominal_col,
cont_col,
transformed=False,
return_scaler=False)
In this specific case, data is time series. So we need the outcome variable (usage in this case) at t+1 as y for all variables at t. To do this, we can use the get_data.preprocess_timesteps function:
trans_data = get_data.preprocess_timesteps(transformed_data,
static_cols_lens=static_cols_lens,
n_in=1,
n_out=1,
groupby=True,
dropnan=True)
Finally, splitting the data into train, val, and test sets can be done using get_data.split_dataset_per_user or get_data.split_dataset functions. This function supports splitting data for regression or classification problems by using regression argument. In this specific case, ID is an important feature for future analysis, so it can be kept by using return_with_ids=True argument.
trainX, valX, testX, \
trainY, valY, testY = \
get_data.split_dataset_per_user(data,
regression=True,
return_train_data=False,
return_with_ids=False)
Define the model
The AttnED function allows several parameters of the model to be defined, including epochs, directory to save trained model, and whether the model should be hypertuned.
model = AttnED(title='EvoSynth_E1',
epochs=200,
directory='tuner/evotion_synth/run',
personalised_prediction=False,
ids_to_predict=17,
regression=True,
hyper_tune=False,
simple_model=False)
Training the model
path = 'saved_models/EvoSynth_E1_bestmodel_v1.h5'
if os.path.exists(path):
bm_path = path
else:
bm_path = model.train_model(trans_trainX,
trans_valX,
trans_trainY,
trans_valY,
name='v1',
verbose=1)
Make predictions
prediction, _ = model.predict(trans_testX_ids,
trans_testY_ids,
scaler,
normaliser,
saved_model_path=bm_path)
Evaluate the model performance
model.get_error_estimators(testY_ids, prediction, trainY)
Explain the model with DiCE
To explain the model with DiCE, a desired range argument needs to be pre-defined.
desired_range = np.array([30000, 40000])
dice = model.explanations(train_data,
trainX_ids,
testX_ids,
trans_trainX_ids,
trans_testX_ids,
trainY_ids,
scaler,
normaliser,
desired_range,
feature_names,
local_instance=0,
saved_model_path=bm_path,
method='dice',
dice_verbose=False)
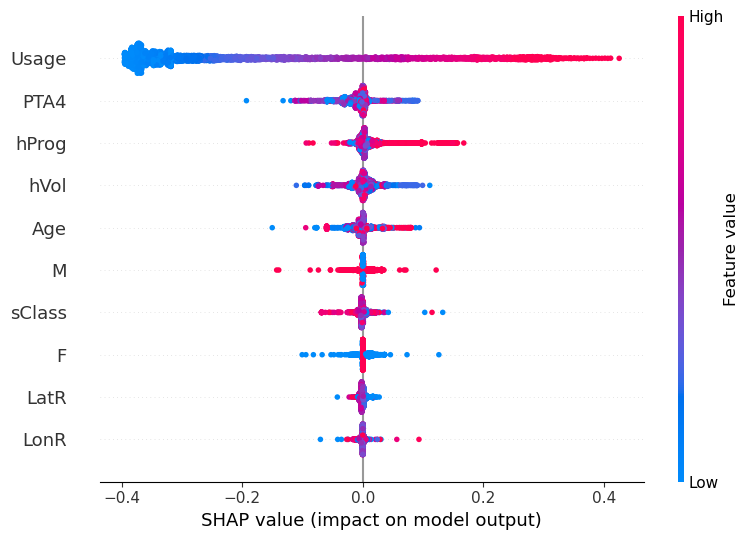
Explain the model with SHAP
shap = model.explanations(data,
trainX_ids,
testX_ids,
trans_trainX_ids,
trans_testX_ids,
trainY_ids,
scaler,
normaliser,
desired_range,
feature_names,
local_instance=0,
saved_model_path=bm_path,
method='shap')
Explain the model with LIME
lime = model.explanations(data,
trainX_ids,
testX_ids,
trans_trainX_ids,
trans_testX_ids,
trainY_ids,
scaler,
normaliser,
desired_range,
feature_names,
local_instance=0,
saved_model_path=bm_path,
method='lime')
SHAP Results
Citing AttnED
@inproceedings{su2022predicting,
title={Predicting and Explaining Hearing Aid Usage Using Encoder-Decoder with Attention Mechanism and SHAP},
author={Su, Qiqi and Iliadou, Eleftheria},
booktitle={2022 16th International Conference on Signal-Image Technology \& Internet-Based Systems (SITIS)},
pages={308--315},
year={2022},
organization={IEEE}
}
